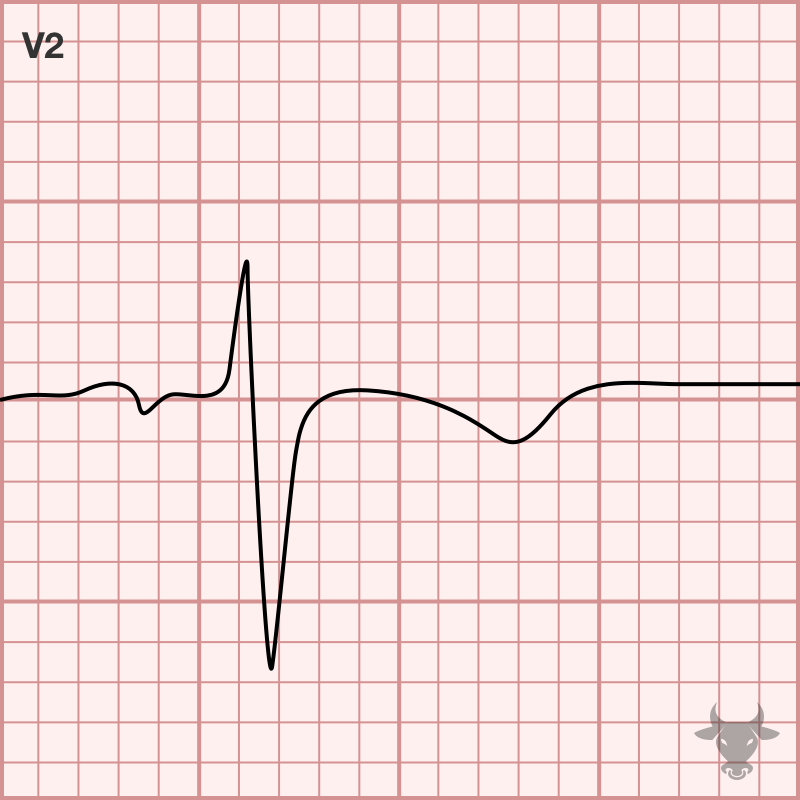
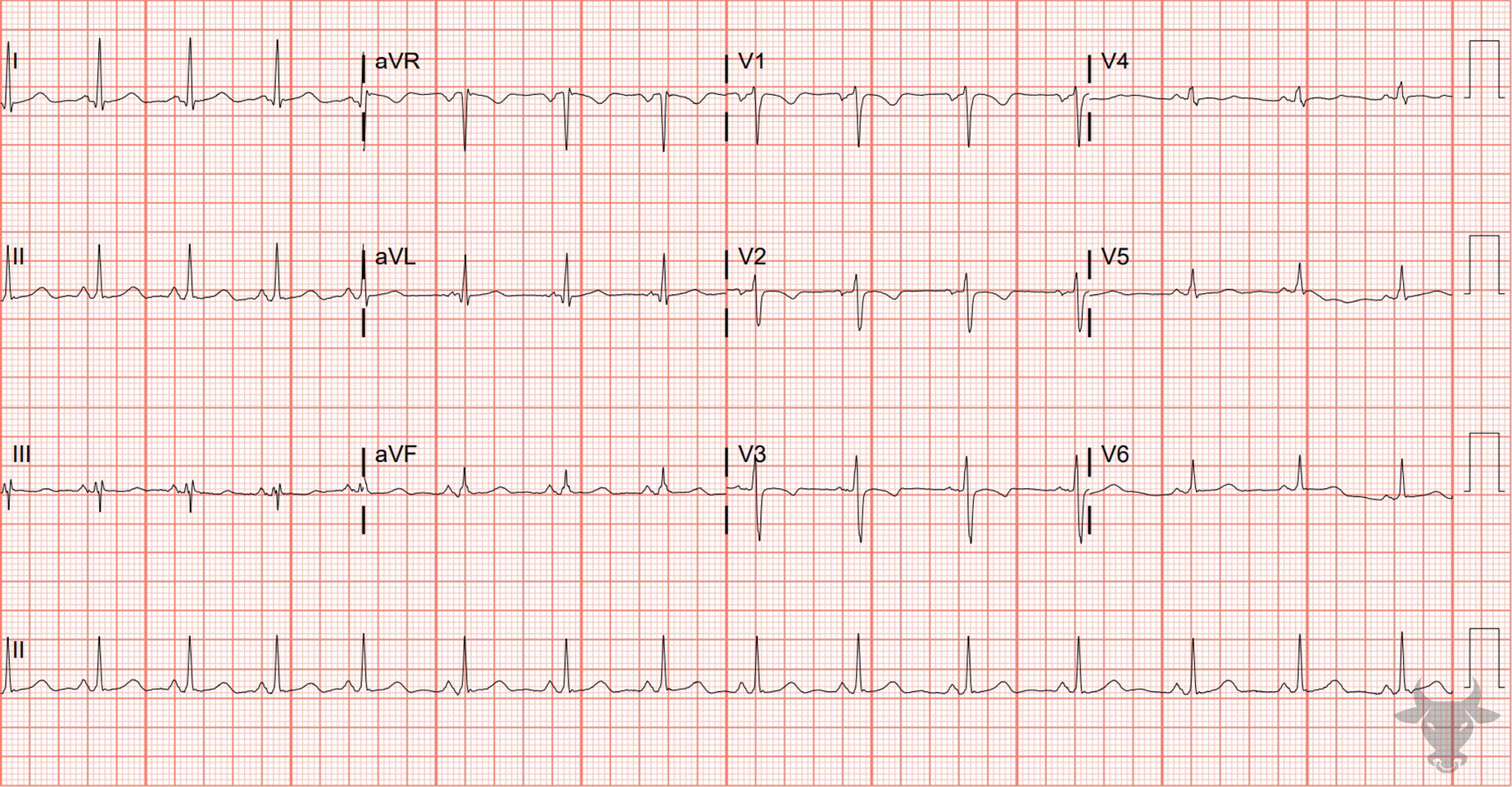
Inverted T-waves in V1-3 are a normal finding in children – the result of right ventricular dominance. While in utero, the neonate’s right ventricle strengthens as it pushes against the pulmonary circulation. After birth, this right ventricular prominence decreases and the juvenile ECG pattern of T-wave inversion in V1-3 gradually evolves into an adult pattern (inversion only in V1) by about age 10.
In some patients, inversions in V1-3 carry on into adulthood. This persistent juvenile T wave pattern is most commonly found in African American women under the age of 30. The pattern does not portend structural changes; it is purely electrical and physiologically normal. While there are no specific diagnostic criteria, the hallmark ECG finding is asymmetric, shallow (< 3 mm), inverted T-waves in leads V1-V3.